What Can You Do About Fallen Arches?
Overview

Fallen arches are very painful and problematic issues with feet of all ages. The easiest way to explain this medical issue that affects millions every year, is that the structural support has loosened or collapsed in the bottom of the foot. The best way to keep prevent arches from falling is to avoid them completely to begin with and there are several preventative steps that can be taken to avoid fallen arches and make sure they're not a part of your everyday life.
Causes
There are many different causes of flat feet, which can be separated into two main categories. The first category, congenital flat foot, is a condition that one is born with or is predisposed to at birth. This type includes the completely asymptomatic, pediatric flexible flat foot-by far the most common form of congenital flat foot. Flexible means that an arch is present until weight is put on the foot, at which time the arch disappears. This foot type is a result of the fact that all people are born with different physical features. Some people have bigger noses than others, just as some people have flatter feet (of course, there is no known correlation between the two). Any alteration in the many building blocks of the foot can influence its shape. At the other end of the spectrum, yet within the same category of congenital flat foot, exist several rare, more severe forms of flat foot. These severe conditions include Vertical Talus, Congenital Calcaneal Valgus, and Tarsal Coalitions - all of which are more rigid (no arch with or without weight on the foot) and definitely symptomatic. Luckily, these are much less common, but can usually be identified by specialists at the time of presentation and treated appropriately. The second category, acquired flat foot, develops over time, rather than at birth. Many different factors can contribute to the development of flat feet. These include the types of shoes a child wears, a child's sitting or sleeping positions, compensation for other abnormalities further up the leg, or more severe factors such as rupture of ligaments or tendons in the foot. Very commonly, the reason for flat feet is that the foot is compensating for a tight Achilles tendon. If the Achilles tendon is tight, then it causes the foot to point down, or to plantarflex (as occurs when stepping on the accelerator of your car). Even minimal amounts of plantarflexion can simulate a longer leg on that particular side, assuming that the other foot is in the normal position. The body therefore tries to compensate by pronating, or flattening out the arch, thereby making up for the perceived extra length on the affected side.
Symptoms
Many people have flat feet and notice no problems and require no treatment. But others may experience the following symptoms, Feet tire easily, painful or achy feet, especially in the areas of the arches and heels, the inside bottom of your feet become swollen, foot movement, such as standing on your toes, is difficult, back and leg pain, If you notice any of these symptoms, it's time for a trip to the doctor.
Diagnosis
If your child has flatfeet, his or her doctor will ask about any family history of flatfeet or inherited foot problems. In a person of any age, the doctor will ask about occupational and recreational activities, previous foot trauma or foot surgery and the type of shoes worn. The doctor will examine your shoes to check for signs of excessive wear. Worn shoes often provide valuable clues to gait problems and poor bone alignment. The doctor will ask you to walk barefoot to evaluate the arches of the feet, to check for out-toeing and to look for other signs of poor foot mechanics. The doctor will examine your feet for foot flexibility and range of motion and feel for any tenderness or bony abnormalities. Depending on the results of this physical examination, foot X-rays may be recommended. X-rays are always performed in a young child with rigid flatfeet and in an adult with acquired flatfeet due to trauma.
bestshoelifts
Non Surgical Treatment
Foot orthotic devices can stabilize some of the causes of flat feet, optimize muscle function and reduce the occurrence of painful symptoms. Generally, a custom-made semi-rigid functional posted orthotic is effective for flat feet. These devices are prescribed based on a thorough biomechanical examination by a qualified chiropodist/podiatrist. Over-the-counter arch supports may be helpful for mild cases, but often prove ineffective to relieve symptoms associated with flatfoot. Wear shoes with a good fit in the arch. Keep active and fit to strengthen leg and foot musculature. Control body weight to decrease load on the feet. Avoid prolonged periods weight bearing with bare feet. Taping to support strained ligaments and joints. Physical therapy modalities such as ultrasound. Referral for surgical correction a severe symptomatic flatfoot.
Surgical Treatment

This is rare and usually only offered if patients have significant abnormalities in their bones or muscles. Treatments include joint fusion, reshaping the bones in the foot, and occasionally moving around tendons in the foot to help balance out the stresses (called tendon transfer).
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.

Fallen arches are very painful and problematic issues with feet of all ages. The easiest way to explain this medical issue that affects millions every year, is that the structural support has loosened or collapsed in the bottom of the foot. The best way to keep prevent arches from falling is to avoid them completely to begin with and there are several preventative steps that can be taken to avoid fallen arches and make sure they're not a part of your everyday life.
Causes
There are many different causes of flat feet, which can be separated into two main categories. The first category, congenital flat foot, is a condition that one is born with or is predisposed to at birth. This type includes the completely asymptomatic, pediatric flexible flat foot-by far the most common form of congenital flat foot. Flexible means that an arch is present until weight is put on the foot, at which time the arch disappears. This foot type is a result of the fact that all people are born with different physical features. Some people have bigger noses than others, just as some people have flatter feet (of course, there is no known correlation between the two). Any alteration in the many building blocks of the foot can influence its shape. At the other end of the spectrum, yet within the same category of congenital flat foot, exist several rare, more severe forms of flat foot. These severe conditions include Vertical Talus, Congenital Calcaneal Valgus, and Tarsal Coalitions - all of which are more rigid (no arch with or without weight on the foot) and definitely symptomatic. Luckily, these are much less common, but can usually be identified by specialists at the time of presentation and treated appropriately. The second category, acquired flat foot, develops over time, rather than at birth. Many different factors can contribute to the development of flat feet. These include the types of shoes a child wears, a child's sitting or sleeping positions, compensation for other abnormalities further up the leg, or more severe factors such as rupture of ligaments or tendons in the foot. Very commonly, the reason for flat feet is that the foot is compensating for a tight Achilles tendon. If the Achilles tendon is tight, then it causes the foot to point down, or to plantarflex (as occurs when stepping on the accelerator of your car). Even minimal amounts of plantarflexion can simulate a longer leg on that particular side, assuming that the other foot is in the normal position. The body therefore tries to compensate by pronating, or flattening out the arch, thereby making up for the perceived extra length on the affected side.
Symptoms
Many people have flat feet and notice no problems and require no treatment. But others may experience the following symptoms, Feet tire easily, painful or achy feet, especially in the areas of the arches and heels, the inside bottom of your feet become swollen, foot movement, such as standing on your toes, is difficult, back and leg pain, If you notice any of these symptoms, it's time for a trip to the doctor.
Diagnosis
If your child has flatfeet, his or her doctor will ask about any family history of flatfeet or inherited foot problems. In a person of any age, the doctor will ask about occupational and recreational activities, previous foot trauma or foot surgery and the type of shoes worn. The doctor will examine your shoes to check for signs of excessive wear. Worn shoes often provide valuable clues to gait problems and poor bone alignment. The doctor will ask you to walk barefoot to evaluate the arches of the feet, to check for out-toeing and to look for other signs of poor foot mechanics. The doctor will examine your feet for foot flexibility and range of motion and feel for any tenderness or bony abnormalities. Depending on the results of this physical examination, foot X-rays may be recommended. X-rays are always performed in a young child with rigid flatfeet and in an adult with acquired flatfeet due to trauma.
bestshoelifts
Non Surgical Treatment
Foot orthotic devices can stabilize some of the causes of flat feet, optimize muscle function and reduce the occurrence of painful symptoms. Generally, a custom-made semi-rigid functional posted orthotic is effective for flat feet. These devices are prescribed based on a thorough biomechanical examination by a qualified chiropodist/podiatrist. Over-the-counter arch supports may be helpful for mild cases, but often prove ineffective to relieve symptoms associated with flatfoot. Wear shoes with a good fit in the arch. Keep active and fit to strengthen leg and foot musculature. Control body weight to decrease load on the feet. Avoid prolonged periods weight bearing with bare feet. Taping to support strained ligaments and joints. Physical therapy modalities such as ultrasound. Referral for surgical correction a severe symptomatic flatfoot.
Surgical Treatment

This is rare and usually only offered if patients have significant abnormalities in their bones or muscles. Treatments include joint fusion, reshaping the bones in the foot, and occasionally moving around tendons in the foot to help balance out the stresses (called tendon transfer).
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.
Leg Length Discrepancy After Total Hip Arthroplasty
Overview
Some people have an ?apparent? LLD which may make the affected leg seem longer than the other leg. There are several factors that can contribute to this feeling. Most commonly, contractures or shortening of the muscles surrounding the hip joint and pelvis make the involved leg feel longer, even when both legs are really the same length. Additionally, contractures of the muscles around the lower back from spinal disorders (i.e. arthritis, spinal stenosis), curvatures of the spine from scoliosis, and deformities of the knee or ankle joint can make one leg seem longer or shorter. In the general public, some people have an ?apparent LLD? as long as one half inch but usually don?t notice it because the LLD occurs over time. A ?true? LLD is where one leg is actually longer than the other. Patients can have unequal leg lengths of 1/4? to 1/2? and never feel it too! You can also have combinations of ?True? and ?Apparent? LLDs. During total hip replacement surgery, the surgeon may ?lengthen? the involved leg by stretching the muscles and ligaments that were contracted, as well as by restoring the joint space that had become narrowed from the arthritis. This is usually a necessary part of the surgery because it also provides stability to the new hip joint. Your surgeon takes measurements of your leg lengths on x-ray prior to surgery. Your surgeon always aims for equal leg lengths if at all possible and measures the length of your legs before and during surgery in order to achieve this goal. Occasionally, surgeons may need to lengthen the operable leg to help improve stability and prevent dislocations as well improve the muscle function around the hip.
Causes
Some children are born with absence or underdeveloped bones in the lower limbs e.g., congenital hemimelia. Others have a condition called hemihypertrophy that causes one side of the body to grow faster than the other. Sometimes, increased blood flow to one limb (as in a hemangioma or blood vessel tumor) stimulates growth to the limb. In other cases, injury or infection involving the epiphyseal plate (growth plate) of the femur or tibia inhibits or stops altogether the growth of the bone. Fractures healing in an overlapped position, even if the epiphyseal plate is not involved, can also cause limb length discrepancy. Neuromuscular problems like polio can also cause profound discrepancies, but thankfully, uncommon. Lastly, Wilms? tumor of the kidney in a child can cause hypertrophy of the lower limb on the same side. It is therefore important in a young child with hemihypertrophy to have an abdominal ultrasound exam done to rule out Wilms? tumor. It is important to distinguish true leg length discrepancy from apparent leg length discrepancy. Apparent discrepancy is due to an instability of the hip, that allows the proximal femur to migrate proximally, or due to an adduction or abduction contracture of the hip that causes pelvic obliquity, so that one hip is higher than the other. When the patient stands, it gives the impression of leg length discrepancy, when the problem is actually in the hip.
Symptoms
Often there are few or no symptoms prior to the age of 25-35. The most common symptom is chronic lower back pain, but also is frequently middle and upper back pain. Same-sided and repeated injury or pain to the hip, knee and/or ankle is also a hallmark of a long-standing untreated LLD. It is not uncommon to have buttock or radiating hip pain that is non-dermatomal (not from a disc) and tends to go away when lying down.
Diagnosis
Leg length discrepancy may be diagnosed during infancy or later in childhood, depending on the cause. Conditions such as hemihypertrophy or hemiatrophy are often diagnosed following standard newborn or infant examinations by a pediatrician, or anatomical asymmetries may be noticed by a child's parents. For young children with hemihypertophy as the cause of their LLD, it is important that they receive an abdominal ultrasound of the kidneys to insure that Wilm's tumor, which can lead to hypertrophy in the leg on the same side, is not present. In older children, LLD is frequently first suspected due to the emergence of a progressive limp, warranting a referral to a pediatric orthopaedic surgeon. The standard workup for LLD is a thorough physical examination, including a series of measurements of the different portions of the lower extremities with the child in various positions, such as sitting and standing. The orthopaedic surgeon will observe the child while walking and performing other simple movements or tasks, such as stepping onto a block. In addition, a number of x-rays of the legs will be taken, so as to make a definitive diagnosis and to assist with identification of the possible etiology (cause) of LLD. Orthopaedic surgeons will compare x-rays of the two legs to the child's age, so as to assess his/her skeletal age and to obtain a baseline for the possibility of excessive growth rate as a cause. A growth chart, which compares leg length to skeletal age, is a simple but essential tool used over time to track the progress of the condition, both before and after treatment. Occasionally, a CT scan or MRI is required to further investigate suspected causes or to get more sophisticated radiological pictures of bone or soft tissue.
Non Surgical Treatment
To begin a path torwards a balanced foundation and reduce pain from leg length discrepancy, ask your doctor about these Functional Orthotics and procedures. Functional Orthotics have been shown to specifically reduce pain from leg length inequality, support all three arches of the foot to create a balanced foundation, maximize shock absorption, add extra propulsion, and supply more stability, enable posture correction and long-term preventive protection. Will improve prolonged effectiveness of chiropractic adjustments. Shoe or heel Lifts, Correct the deficiencies that causes imbalances in the body.

leg length discrepancy symptoms
Surgical Treatment
Limb deformity or leg length problems can be treated by applying an external frame to the leg. The frame consists of metal rings which go round the limb. The rings are held onto the body by wires and metal pins which pass through the skin and are anchored into the bone. During this operation, the bone is divided. Gradual adjustment of the frame results in creation of a new bone allowing a limb to be lengthened. The procedure involves the child having an anaesthetic. The child is normally in hospital for one week. The child and family are encouraged to clean pin sites around the limb. The adjustments of the frame (distractions) are performed by the child and/or family. The child is normally encouraged to walk on the operated limb and to actively exercise the joints above and below the frame. The child is normally reviewed on a weekly basis in clinic to monitor the correction of the deformity. The frame normally remains in place for 3 months up to one year depending on the condition which is being treated. The frame is normally removed under a general anaesthetic at the end of treatment.
Some people have an ?apparent? LLD which may make the affected leg seem longer than the other leg. There are several factors that can contribute to this feeling. Most commonly, contractures or shortening of the muscles surrounding the hip joint and pelvis make the involved leg feel longer, even when both legs are really the same length. Additionally, contractures of the muscles around the lower back from spinal disorders (i.e. arthritis, spinal stenosis), curvatures of the spine from scoliosis, and deformities of the knee or ankle joint can make one leg seem longer or shorter. In the general public, some people have an ?apparent LLD? as long as one half inch but usually don?t notice it because the LLD occurs over time. A ?true? LLD is where one leg is actually longer than the other. Patients can have unequal leg lengths of 1/4? to 1/2? and never feel it too! You can also have combinations of ?True? and ?Apparent? LLDs. During total hip replacement surgery, the surgeon may ?lengthen? the involved leg by stretching the muscles and ligaments that were contracted, as well as by restoring the joint space that had become narrowed from the arthritis. This is usually a necessary part of the surgery because it also provides stability to the new hip joint. Your surgeon takes measurements of your leg lengths on x-ray prior to surgery. Your surgeon always aims for equal leg lengths if at all possible and measures the length of your legs before and during surgery in order to achieve this goal. Occasionally, surgeons may need to lengthen the operable leg to help improve stability and prevent dislocations as well improve the muscle function around the hip.

Causes
Some children are born with absence or underdeveloped bones in the lower limbs e.g., congenital hemimelia. Others have a condition called hemihypertrophy that causes one side of the body to grow faster than the other. Sometimes, increased blood flow to one limb (as in a hemangioma or blood vessel tumor) stimulates growth to the limb. In other cases, injury or infection involving the epiphyseal plate (growth plate) of the femur or tibia inhibits or stops altogether the growth of the bone. Fractures healing in an overlapped position, even if the epiphyseal plate is not involved, can also cause limb length discrepancy. Neuromuscular problems like polio can also cause profound discrepancies, but thankfully, uncommon. Lastly, Wilms? tumor of the kidney in a child can cause hypertrophy of the lower limb on the same side. It is therefore important in a young child with hemihypertrophy to have an abdominal ultrasound exam done to rule out Wilms? tumor. It is important to distinguish true leg length discrepancy from apparent leg length discrepancy. Apparent discrepancy is due to an instability of the hip, that allows the proximal femur to migrate proximally, or due to an adduction or abduction contracture of the hip that causes pelvic obliquity, so that one hip is higher than the other. When the patient stands, it gives the impression of leg length discrepancy, when the problem is actually in the hip.
Symptoms
Often there are few or no symptoms prior to the age of 25-35. The most common symptom is chronic lower back pain, but also is frequently middle and upper back pain. Same-sided and repeated injury or pain to the hip, knee and/or ankle is also a hallmark of a long-standing untreated LLD. It is not uncommon to have buttock or radiating hip pain that is non-dermatomal (not from a disc) and tends to go away when lying down.
Diagnosis
Leg length discrepancy may be diagnosed during infancy or later in childhood, depending on the cause. Conditions such as hemihypertrophy or hemiatrophy are often diagnosed following standard newborn or infant examinations by a pediatrician, or anatomical asymmetries may be noticed by a child's parents. For young children with hemihypertophy as the cause of their LLD, it is important that they receive an abdominal ultrasound of the kidneys to insure that Wilm's tumor, which can lead to hypertrophy in the leg on the same side, is not present. In older children, LLD is frequently first suspected due to the emergence of a progressive limp, warranting a referral to a pediatric orthopaedic surgeon. The standard workup for LLD is a thorough physical examination, including a series of measurements of the different portions of the lower extremities with the child in various positions, such as sitting and standing. The orthopaedic surgeon will observe the child while walking and performing other simple movements or tasks, such as stepping onto a block. In addition, a number of x-rays of the legs will be taken, so as to make a definitive diagnosis and to assist with identification of the possible etiology (cause) of LLD. Orthopaedic surgeons will compare x-rays of the two legs to the child's age, so as to assess his/her skeletal age and to obtain a baseline for the possibility of excessive growth rate as a cause. A growth chart, which compares leg length to skeletal age, is a simple but essential tool used over time to track the progress of the condition, both before and after treatment. Occasionally, a CT scan or MRI is required to further investigate suspected causes or to get more sophisticated radiological pictures of bone or soft tissue.
Non Surgical Treatment
To begin a path torwards a balanced foundation and reduce pain from leg length discrepancy, ask your doctor about these Functional Orthotics and procedures. Functional Orthotics have been shown to specifically reduce pain from leg length inequality, support all three arches of the foot to create a balanced foundation, maximize shock absorption, add extra propulsion, and supply more stability, enable posture correction and long-term preventive protection. Will improve prolonged effectiveness of chiropractic adjustments. Shoe or heel Lifts, Correct the deficiencies that causes imbalances in the body.

leg length discrepancy symptoms
Surgical Treatment
Limb deformity or leg length problems can be treated by applying an external frame to the leg. The frame consists of metal rings which go round the limb. The rings are held onto the body by wires and metal pins which pass through the skin and are anchored into the bone. During this operation, the bone is divided. Gradual adjustment of the frame results in creation of a new bone allowing a limb to be lengthened. The procedure involves the child having an anaesthetic. The child is normally in hospital for one week. The child and family are encouraged to clean pin sites around the limb. The adjustments of the frame (distractions) are performed by the child and/or family. The child is normally encouraged to walk on the operated limb and to actively exercise the joints above and below the frame. The child is normally reviewed on a weekly basis in clinic to monitor the correction of the deformity. The frame normally remains in place for 3 months up to one year depending on the condition which is being treated. The frame is normally removed under a general anaesthetic at the end of treatment.
Heel Pain All You Might Want To Understand Heel Pain
Overview

Heel pain is common and can be due to a number of conditions. The calcaneus (heel bone) is the largest bone in the foot and is the first to hit the ground when walking. The heel bone is designed to be the first contact the foot has with the ground. The achilles tendon inserts into the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) and a very strong ligament along the bottom of the foot attaches to the bottom of the heel bone (the plantar fascia). Several small muscles also attach to the heel bone above the insertion of the plantar fascia. Given the forces of walking that the heel bone is subjected to and the pull of all these ligaments and muscles, then it is not surprising that heel pain is so common.
Causes
Long standing inflammation causes the deposition of calcium at the point where the plantar fascia inserts into the heel. This results in the appearance of a sharp thorn like heel spur on x-ray. The heel spur is asymptomatic (not painful), the pain arises from the inflammation of the plantar fascia.
Symptoms
Usually worse with the first few steps in the morning or at the initial point of activity. The latter usually gets better with continued activity (squeaky hinge analogy). Walking, running, sprinting, hill running and jumping will increase the pain. Often, the natural response is to walk on the outside of the foot - in supination - to lessen the stress on the plantar fascia - resulting in new problems.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist (doctor who specializes in the evaluation and treatment of foot diseases) will carry out a physical examination, and ask pertinent questions about the pain. The doctor will also ask the patient how much walking and standing the patient does, what type of footwear is worn, and details of the his/her medical history. Often this is enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes further diagnostic tests are needed, such as blood tests and imaging scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
If pain and other symptoms of inflammation?redness, swelling, heat?persist, you should limit normal daily activities and contact a doctor of podiatric medicine. The podiatric physician will examine the area and may perform diagnostic X-rays to rule out problems of the bone. Early treatment might involve oral or injectable anti-inflammatory medication, exercise and shoe recommendations, taping or strapping, or use of shoe inserts or orthotic devices. Taping or strapping supports the foot, placing stressed muscles and tendons in a physiologically restful state. Physical therapy may be used in conjunction with such treatments. A functional orthotic device may be prescribed for correcting biomechanical imbalance, controlling excessive pronation, and supporting of the ligaments and tendons attaching to the heel bone. It will effectively treat the majority of heel and arch pain without the need for surgery. Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require more advanced treatments or surgery. If surgery is necessary, it may involve the release of the plantar fascia, removal of a spur, removal of a bursa, or removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
heel pain pads
Prevention

You can try to avoid the things that cause heel pain to start avoid becoming overweight, where your job allows, minimise the shock to your feet from constant pounding on hard surfaces, reduce the shocks on your heel by choosing footwear with some padding or shock-absorbing material in the heel, if you have high-arched feet or flat feet a moulded insole in your shoe may reduce the stresses on your feet, if you have an injury to your ankle or foot, make sure you exercise afterwards to get back as much movement as possible to reduce the stresses on your foot and your heel in particular, If you start to get heel pain, doing the above things may enable the natural healing process to get underway and the pain to improve.

Heel pain is common and can be due to a number of conditions. The calcaneus (heel bone) is the largest bone in the foot and is the first to hit the ground when walking. The heel bone is designed to be the first contact the foot has with the ground. The achilles tendon inserts into the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) and a very strong ligament along the bottom of the foot attaches to the bottom of the heel bone (the plantar fascia). Several small muscles also attach to the heel bone above the insertion of the plantar fascia. Given the forces of walking that the heel bone is subjected to and the pull of all these ligaments and muscles, then it is not surprising that heel pain is so common.
Causes
Long standing inflammation causes the deposition of calcium at the point where the plantar fascia inserts into the heel. This results in the appearance of a sharp thorn like heel spur on x-ray. The heel spur is asymptomatic (not painful), the pain arises from the inflammation of the plantar fascia.
Symptoms
Usually worse with the first few steps in the morning or at the initial point of activity. The latter usually gets better with continued activity (squeaky hinge analogy). Walking, running, sprinting, hill running and jumping will increase the pain. Often, the natural response is to walk on the outside of the foot - in supination - to lessen the stress on the plantar fascia - resulting in new problems.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist (doctor who specializes in the evaluation and treatment of foot diseases) will carry out a physical examination, and ask pertinent questions about the pain. The doctor will also ask the patient how much walking and standing the patient does, what type of footwear is worn, and details of the his/her medical history. Often this is enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes further diagnostic tests are needed, such as blood tests and imaging scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
If pain and other symptoms of inflammation?redness, swelling, heat?persist, you should limit normal daily activities and contact a doctor of podiatric medicine. The podiatric physician will examine the area and may perform diagnostic X-rays to rule out problems of the bone. Early treatment might involve oral or injectable anti-inflammatory medication, exercise and shoe recommendations, taping or strapping, or use of shoe inserts or orthotic devices. Taping or strapping supports the foot, placing stressed muscles and tendons in a physiologically restful state. Physical therapy may be used in conjunction with such treatments. A functional orthotic device may be prescribed for correcting biomechanical imbalance, controlling excessive pronation, and supporting of the ligaments and tendons attaching to the heel bone. It will effectively treat the majority of heel and arch pain without the need for surgery. Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require more advanced treatments or surgery. If surgery is necessary, it may involve the release of the plantar fascia, removal of a spur, removal of a bursa, or removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
heel pain pads
Prevention

You can try to avoid the things that cause heel pain to start avoid becoming overweight, where your job allows, minimise the shock to your feet from constant pounding on hard surfaces, reduce the shocks on your heel by choosing footwear with some padding or shock-absorbing material in the heel, if you have high-arched feet or flat feet a moulded insole in your shoe may reduce the stresses on your feet, if you have an injury to your ankle or foot, make sure you exercise afterwards to get back as much movement as possible to reduce the stresses on your foot and your heel in particular, If you start to get heel pain, doing the above things may enable the natural healing process to get underway and the pain to improve.
Mortons Neuroma Prevention
Overview
 Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Causes
Morton's Neuroma is a caused by pressure, abnormal function/motion or an imbalance in the structure of the foot such as flat feet, that causes an abnormal pressure on the structures and the nerves in the ball of the foot. It most commonly affects the nerve that goes to the 2nd 3rd or 4th toes. The squeezing of the nerve from abnormal motion leads to a protective thickening of the sheath that protects the nerve. Symptoms of Morton's Neuroma often occur during or after activities that cause a sidewards squeezing of the ball of the foot or from pressure such as walking, standing, or playing sport. Since squeezing is a common cause of the condition, shoes such as pointed toes or high heels can often lead to a neuroma. Shoes that are constricting, even tight sneakers, can pinch the nerve between the toes, causing inflammation and pain.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Morton?s Neuroma tend to come and go over time. They are typically exacerbated by physical activity or by wearing certain shoes. Morton?s Neuroma symptoms include sharp pain in the ball of the foot, pain radiating to the tips of the toes, burning pain in the second, third, or fourth toes, numbness in the toes, sensation of a lump between the toes.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of interdigital neuroma is usually made by physical examination and review of the patient's medical history.MRI ad High Definition Ultrasound examination may be useful to confirm the diagnoses however they may still not be 100% reliable. The commonest reason for this is de to natural substances present in between the metatarsal heads and between the fat pad and the intermetatarsal ligament. These natural substances i.e. bursa, fat, capsular thickening and even bony growths, can all be a factor in the impingement process and may need to be surgically cleared.
Non Surgical Treatment
Ice therapy and anti-inflammatory medications or supplements. If conservative care measures fail to resolve your problem, some foot care providers may recommend a cortisone injection around your involved nerve to help reduce your swelling and inflammation. Concentrated alcohol injections around your affected nerve have also shown good results and should be considered before undergoing neurectomy, a surgical procedure to remove the enlarged, traumatized portion of your involved nerve.
Surgical Treatment
When early treatments fail and the neuroma progresses past the threshold for such options, podiatric surgery may become necessary. The procedure, which removes the inflamed and enlarged nerve, can usually be conducted on an outpatient basis, with a recovery time that is often just a few weeks. Your podiatric physician will thoroughly describe the surgical procedures to be used and the results you can expect. Any pain following surgery is easily managed with medications prescribed by your podiatrist.
Prevention
Wearing proper footwear that minimizes compression of the forefoot can help to prevent the development of and aggravation of a Morton's neuroma.
 Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.Causes
Morton's Neuroma is a caused by pressure, abnormal function/motion or an imbalance in the structure of the foot such as flat feet, that causes an abnormal pressure on the structures and the nerves in the ball of the foot. It most commonly affects the nerve that goes to the 2nd 3rd or 4th toes. The squeezing of the nerve from abnormal motion leads to a protective thickening of the sheath that protects the nerve. Symptoms of Morton's Neuroma often occur during or after activities that cause a sidewards squeezing of the ball of the foot or from pressure such as walking, standing, or playing sport. Since squeezing is a common cause of the condition, shoes such as pointed toes or high heels can often lead to a neuroma. Shoes that are constricting, even tight sneakers, can pinch the nerve between the toes, causing inflammation and pain.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Morton?s Neuroma tend to come and go over time. They are typically exacerbated by physical activity or by wearing certain shoes. Morton?s Neuroma symptoms include sharp pain in the ball of the foot, pain radiating to the tips of the toes, burning pain in the second, third, or fourth toes, numbness in the toes, sensation of a lump between the toes.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of interdigital neuroma is usually made by physical examination and review of the patient's medical history.MRI ad High Definition Ultrasound examination may be useful to confirm the diagnoses however they may still not be 100% reliable. The commonest reason for this is de to natural substances present in between the metatarsal heads and between the fat pad and the intermetatarsal ligament. These natural substances i.e. bursa, fat, capsular thickening and even bony growths, can all be a factor in the impingement process and may need to be surgically cleared.
Non Surgical Treatment
Ice therapy and anti-inflammatory medications or supplements. If conservative care measures fail to resolve your problem, some foot care providers may recommend a cortisone injection around your involved nerve to help reduce your swelling and inflammation. Concentrated alcohol injections around your affected nerve have also shown good results and should be considered before undergoing neurectomy, a surgical procedure to remove the enlarged, traumatized portion of your involved nerve.

Surgical Treatment
When early treatments fail and the neuroma progresses past the threshold for such options, podiatric surgery may become necessary. The procedure, which removes the inflamed and enlarged nerve, can usually be conducted on an outpatient basis, with a recovery time that is often just a few weeks. Your podiatric physician will thoroughly describe the surgical procedures to be used and the results you can expect. Any pain following surgery is easily managed with medications prescribed by your podiatrist.
Prevention
Wearing proper footwear that minimizes compression of the forefoot can help to prevent the development of and aggravation of a Morton's neuroma.
Shoe Lifts The Podiatrists Answer For Leg Length Discrepancy
There are actually not one but two unique variations of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital indicates that you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter in comparison to the other. Through developmental phases of aging, the brain senses the stride pattern and identifies some difference. The body usually adapts by tilting one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of under a quarter inch isn't very uncommon, require Shoe Lifts to compensate and normally does not have a serious effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiscovered on a daily basis, however this condition is easily remedied, and can eradicate a number of incidents of lower back pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality commonly consists of Shoe Lifts . These are typically affordable, in most cases being below twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or even more. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position.
Chronic back pain is the most prevalent ailment impacting men and women today. Around 80 million people experience back pain at some stage in their life. It is a problem which costs businesses millions annually on account of lost time and production. Fresh and superior treatment solutions are constantly sought after in the hope of decreasing the economic influence this issue causes.

People from all corners of the earth suffer the pain of foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these cases Shoe Lifts are usually of worthwhile. The lifts are capable of easing any pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless qualified orthopaedic physicians.
In order to support the human body in a well balanced fashion, feet have got a significant part to play. Irrespective of that, it's often the most neglected region of the human body. Some people have flat-feet meaning there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This causes other body parts like knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that proper posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiscovered on a daily basis, however this condition is easily remedied, and can eradicate a number of incidents of lower back pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality commonly consists of Shoe Lifts . These are typically affordable, in most cases being below twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or even more. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position.
Chronic back pain is the most prevalent ailment impacting men and women today. Around 80 million people experience back pain at some stage in their life. It is a problem which costs businesses millions annually on account of lost time and production. Fresh and superior treatment solutions are constantly sought after in the hope of decreasing the economic influence this issue causes.

People from all corners of the earth suffer the pain of foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these cases Shoe Lifts are usually of worthwhile. The lifts are capable of easing any pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless qualified orthopaedic physicians.
In order to support the human body in a well balanced fashion, feet have got a significant part to play. Irrespective of that, it's often the most neglected region of the human body. Some people have flat-feet meaning there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This causes other body parts like knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that proper posture and balance are restored.
What Is The Ideal Solution For Inferior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
Heel spurs are a common reason for people to visit their podiatrist serving Scottsdale. These small calcium deposits can cause major pain, but treatments are available to relieve your symptoms. Heel spurs grow along the plantar fascia and create a sensation similar to that of a pebble being stuck in your shoe. Your podiatrist will use a physical exam plus X-rays to determine if a heel spur is the cause of your foot pain before beginning treatment. If you do have a heel spur, your podiatrist may recommend a cortisone injection to ease inflammation. Other techniques, such as stretching the calf muscles, treating the heel with ice, and wearing a custom orthotic may also provide relief from the discomfort of a heel spur.
Causes
Heel spurs under the sole of the foot (plantar area) are associated with inflammation of the plantar fascia (fasciitis), the "bowstring-like" tissue stretching underneath the sole that attaches at the heel. Plantar heel spurs cause localized tenderness and pain made worse when stepping down on the heel. Heel spurs and plantar fasciitis can occur alone or be related to underlying diseases that cause arthritis (inflammation of the joints), such as reactive arthritis (formerly called Reiter's disease), ankylosing spondylitis, and diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. It is important to note that heel spurs may cause no symptoms at all and may be incidentally discovered during X-ray exams taken for other purposes.
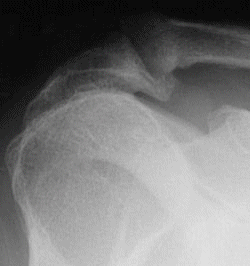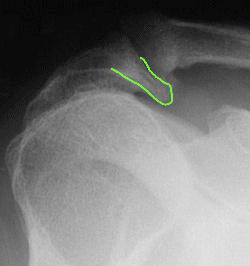
Symptoms
Most bone spurs cause no signs or symptoms. You might not realize you have bone spurs until an X-ray for another condition reveals the growths. In some cases, though, bone spurs can cause pain and loss of motion in your joints.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made using a few different technologies. X-rays are often used first to ensure there is no fracture or tumor in the region. Then ultrasound is used to check the fascia itself to make sure there is no tear and check the level of scar tissue and damage. Neurosensory testing, a non-painful nerve test, can be used to make sure there is not a local nerve problem if the pain is thought to be nerve related. It is important to remember that one can have a very large heel spur and no plantar fasciitis issues or pain at all, or one can have a great deal of pain and virtually no spur at all.
Non Surgical Treatment
Heel spurs are considered a self-limited condition, which means that by making small alterations in your lifestyle and regular routines you can often control the condition. The goal is to relieve pain, reduce friction and transfer pressure from your sensitive foot areas. By eliminating the cause of the heel spur and plantar fasciitis (i.e. better shoes, orthotics to fix your gait, losing weight) will help reduce the pressure put on your fascia and heel and can reduce the inflammation caused by your heel spur. Failure to see improvements after conservative treatments may make surgery your only option.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is used a very small percentage of the time. It is usually considered after trying non-surgical treatments for at least a year. Plantar fascia release surgery is use to relax the plantar fascia. This surgery is commonly paired with tarsal tunnel release surgery. Surgery is successful for the majority of people.
Prevention
To prevent this condition, wearing properly fitted shoes with good arch support is very important. If a person is overweight, weight loss can help diminish stress on the feet and help prevent foot problems. For those who exercise frequently and intensely, proper stretching is always necessary, especially when there is an increase in activities or a change in running technique. It is not recommended to attempt to work through the pain, as this can change a mild case of heel spurs and plantar fascitis into a long-lasting and painful episode of the condition.
What Is Calcaneal Spur

Overview
Although a heel spur is often thought to be the source of heel pain, it rarely is. When a patient has plantar fasciitis, the plantar fascia pulls on the bottom of the heel bone. Over time this can cause a spur to form. Heels spurs are a very common x-ray finding, and because the heel spur is buried deep in soft tissue and not truly in a weight bearing area, there is often no history of pain. It is important to note that less than one percent of all heel pain is due to a spur. but frequently caused by the plantar fascia pulling on the heel. Once the plantar fasciitis is properly treated, the heel spur could be a distant memory.
Causes
An individual with the lower legs angulating inward, a condition called genu valgum or "knock knees," can have a tendency toward excessive pronation. As a result, this too can lead to a fallen arch resulting in plantar fascitis and heel spurs. Women tend to have more genu valgum than men do. Heel spurs can also result from an abnormally high arch. Other factors leading to heel spurs include a sudden increase in daily activities, an increase in weight, or a change of shoes. Dramatic increase in training intensity or duration may cause plantar fascitis. Shoes that are too flexible in the middle of the arch or shoes that bend before the toe joints will cause an increase in tension in the plantar fascia and possibly lead to heel spurs.
Symptoms
Most heel spurs cause no symptoms and may go undetected for years. If they cause no pain or discomfort, they require no treatment. Occasionally, a bone spur will break off from the larger bone, becoming a ?loose body?, floating in a joint or embedding itself in the lining of the joint. This can cause pain and intermittent locking of the joint. In the case of heel spurs, sharp pain and discomfort is felt on the bottom of the foot or heel.
Diagnosis
Your doctor, when diagnosing and treating this condition will need an x-ray and sometimes a gait analysis to ascertain the exact cause of this condition. If you have pain in the bottom of your foot and you do not have diabetes or a vascular problem, some of the over-the-counter anti-inflammatory products such as Advil or Ibuprofin are helpful in eradicating the pain. Pain creams, such as Neuro-eze, BioFreeze & Boswella Cream can help to relieve pain and help increase circulation.
Non Surgical Treatment
The key for the proper treatment of heel spurs is determining what is causing the excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. When the cause is over-pronation (flat feet), an orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support is an effective device to reduce the over-pronation, and allow the condition to heal. Other common treatments include stretching exercises, losing weight, wearing shoes that have a cushioned heel that absorbs shock, and elevating the heel with the use of a heel cradle, heel cup, or orthotic. Heel cradles and heel cups provide extra comfort and cushion to the heel, and reduce the amount of shock and shear forces experienced from everyday activities.
Surgical Treatment
Approximately 2% of people with painful heel spurs need surgery, meaning that 98 out of 100 people do well with the non-surgical treatments previously described. However, these treatments can sometimes be rather long and drawn out, and may become considerably expensive. Surgery should be considered when conservative treatment is unable to control and prevent the pain. If the pain goes away for a while, and continues to come back off and on, despite conservative treatments, surgery should be considered. If the pain really never goes away, but reaches a plateau, beyond which it does not improve despite conservative treatments, surgery should be considered. If the pain requires three or more injections of "cortisone" into the heel within a twelve month period, surgery should be considered.
Prevention
In 2002, researchers attempted to compare the effects of various running techniques on pronation and resulting injuries like stress fractures and heel spurs. They suggested that it is possible to teach runners to stride in such a way as to minimize impact forces. One way is to lower running speed. Another is to take longer rest periods following a run.